 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Optical properties: Exciton effects |
When light is absorbed by materials, a pair of an electron with negative charge and a hole with positive charge is created. Since in one-dimensional systems like carbon nanotubes, Coulomb interactions are important, this electron-hole pair forms a bound state called an exciton and effects of excitons are important. We revealed characteristic effects of excitons in quasi-one-dimensional systems.
When light whose polarization is perpendicular to the nanotube axis is irradiated to a carbon nanotube, positive and negative charges are separated on the opposite sides of a cross section of the nanotube, leading to depolarization effects, which weaken the external electric field. Thus it has been considered that light with the perpendicular polarization is negligibly absorbed by nanotubes. However, we showed that because of strong Coulomb interactions, exciton peaks can appear in the optical absorption spectra of carbon nanotubes even for perpendicular polarization. |
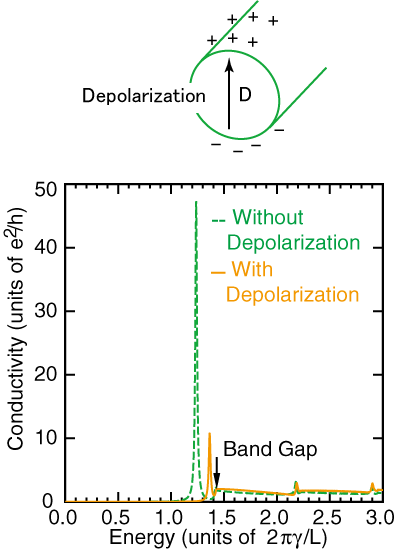 |
| Optical absorption spectra for perpendicular polarization. The units of energy is a typical kinetic energy. A peak appears below an absorption band even when the depolarization effects are considered (Orange solid line). |
| Reference |
| S. Uryu and T. Ando, Phys. Rev. B 74, 155411 (2006). |
 |
 |
 |
| Copyright (C) Seiji URYU, All rights reserved. |
|
 |
|